重庆科技学院冶金与材料工程学院, 重庆 401331
本文提出了一种简便、可规模化制备CoO纳米线@C/碳布(CC)复合材料的方法, 该复合材料可用作无粘结剂锂离子电池负极。首先通过简单的水热和煅烧法制备了CoO纳米线@碳布复合材料, 再通过葡萄糖溶液浸渍和煅烧获得具有三维立体结构的CoO纳米线@C/CC复合电极材料。碳包覆的CoO纳米线均匀地分散在碳布上, 形成导电的碳网络。在碳布上原位生长的CoO纳米线可以有效缩短锂离子的转移路径, 降低接触电阻。碳涂层厚度约为1 nm, 显著抑制了锂离子嵌入/嵌出过程中活性材料的粉碎, 以及CoO在电解液中的直接暴露。结果表明CoO纳米线@C/CC复合材料用作锂离子电池的无粘结剂负极时, 具有良好的充放电性能和循环稳定性。电流密度为1 A·cm-2时, 200次循环后的比容量为863 mAh·cm-2(容量保持率75.83%)。本研究为柔性锂离子电池负极材料的制备提供了一种可行的新选择。
CoO纳米线 碳包覆 柔性 锂离子电池 负极 CoO nanowire carbon coating flexible lithium-ion battery anode

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Integrated Circuits, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Integrated Circuits, Beijing 100871, China
3 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronics Technology, Ministry of Education, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China
The finding of the robust ferroelectricity in HfO2-based thin films is fantastic from the view point of both the fundamentals and the applications. In this review article, the current research status of the future prospects for the ferroelectric HfO2-based thin films and devices are presented from fundamentals to applications. The related issues are discussed, which include: 1) The ferroelectric characteristics observed in HfO2-based films and devices associated with the factors of dopant, strain, interface, thickness, defect, fabrication condition, and more; 2) physical understanding on the observed ferroelectric behaviors by the density functional theory (DFT)-based theory calculations; 3) the characterizations of microscopic and macroscopic features by transmission electron microscopes-based and electrical properties-based techniques; 4) modeling and simulations, 5) the performance optimizations, and 6) the applications of some ferroelectric-based devices such as ferroelectric random access memory, ferroelectric-based field effect transistors, and the ferroelectric tunnel junction for the novel information processing systems.
ferroelectricity HfO2-based thin films physical mechanism characterization modeling and simulation applications Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(5): 053101
强激光与粒子束
2022, 34(7): 075009
重庆科技学院冶金与材料工程学院, 重庆 401331
可穿戴、可折叠电子设备日益受到人们的关注, 开发与之配套的柔性电极材料成为当下的研究热点。本研究采用水热法制备前驱体/碳布复合材料, 将其在高纯氩气气氛下煅烧, 得到柔性的CoO多孔纳米片阵列/碳布负极材料。这种多孔与三维网状立体结构能够有效缓解充放电过程中材料的体积效应, 而且多孔结构还增加了活性物质CoO纳米片的比表面积, 有利于电极材料储锂容量的提升。电化学性能测试表明, 该CoO多孔纳米片阵列/碳布负极材料在100 mA·cm-2的恒电流下, 首次放电容量1 862.8 mAh·cm-2, 首次循环库伦效率87.8%, 在700 mA·cm-2的电流密度下, 经过100次的充放电循环后, 材料的放电比容量仍保持在1 428.9 mAh·cm-2。在1 000 mA·cm-2的电流密度下, 仍然有1 353.8 mAh·cm2的容量。该方法简便易行且原料成本低廉, 可以降低锂离子电池柔性负极材料的成本。
CoO多孔纳米片 碳布 柔性电极材料 负极材料 水热法 电化学性能 CoO porous nanosheet carbon cloth flexible electrode material anode material hydrothermal method electrochemical performance
1 齐鲁工业大学(山东省科学院)山东省科学院海洋仪器仪表研究所 山东省海洋监测仪器装备技术重点实验室 国家海洋监测设备工程技术研究中心,山东 青岛 266100
2 热带海洋环境国家重点实验室 中国科学院南海海洋研究所,广东 广州 510301
针对目前透明度遥感反演研究多以较低空间分辨率卫星数据为主的现状,采用分辨率高达10 m的Sentinel-2卫星数据进行了胶州湾海域水体透明度的遥感反演研究。构建了基于实测数据的反演模型。结果表明:模型具有较高的精度,反演值与实测值的平均相对误差为9.86%,均方根误差为0.22 m。依据构建的反演模型与卫星影像数据反演了胶州湾水体的透明度,绘制了水体的透明度分布图,分析了胶州湾海域水体透明度的空间分布规律和局部的细微变化特征。研究发现,胶州湾海域水体透明度呈现由近岸向外海逐渐升高的趋势,径流量大的河流会造成汇入海域透明度明显降低的变化,潮汐会引起透明度出现沿垂直于岸边方向的纹理变化特征,大型船只的通航会造成透明度短时降低的变化。
透明度 哨兵2号 遥感反演 胶州湾 SDD Sentinel-2 remote sensing retrieval Jiaozhou Bay 红外与激光工程
2021, 50(12): 20210080
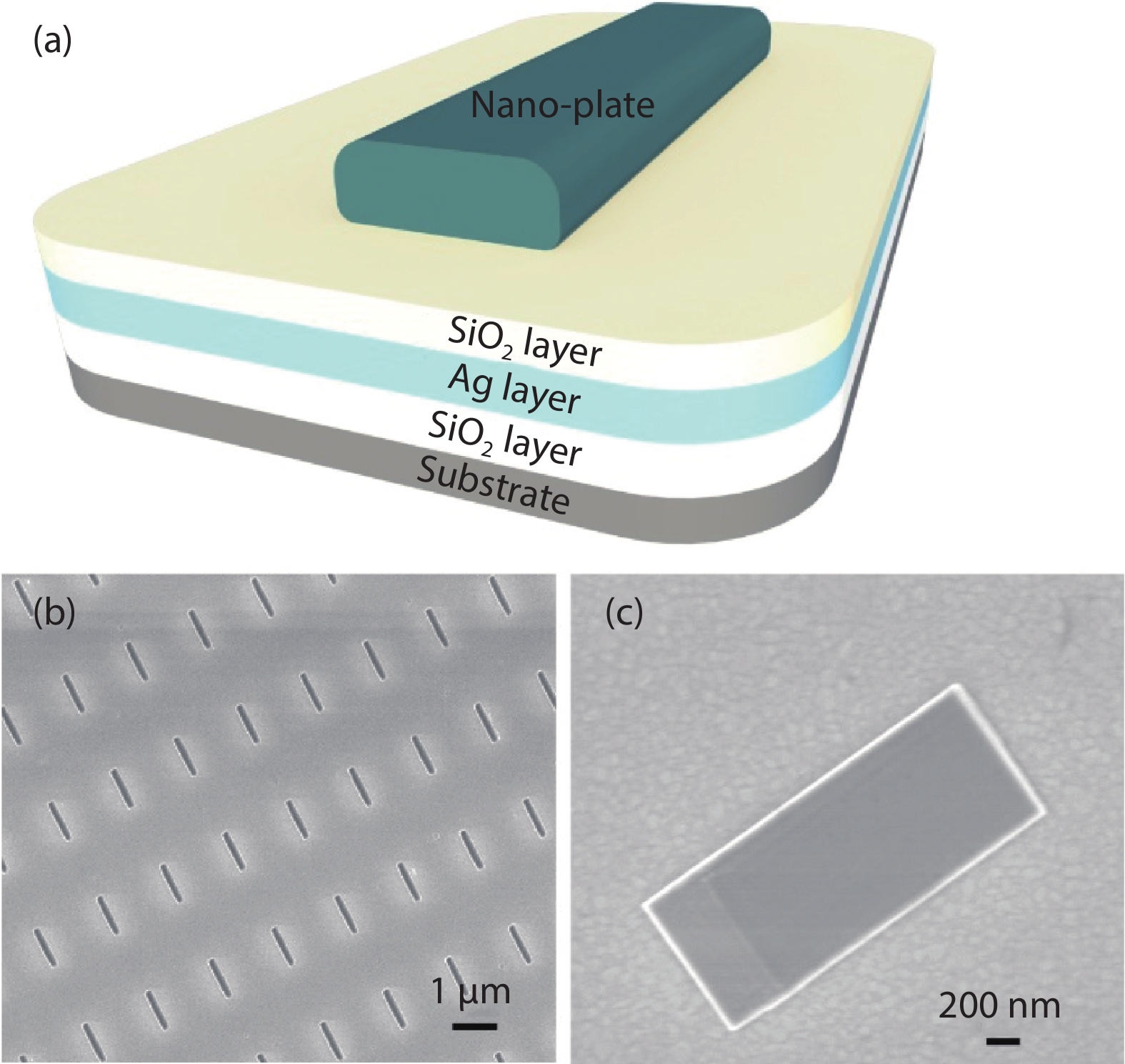
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronic and Optical Engineering, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
2 College of Microelectronics, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
3 Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Advanced Photonic and Electronic Materials, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
4 Nanjing National Laboratory of Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
5 School of Information Science and Technology, Nantong University, Nantong 226019, China
6 Tongke School of Microelectronics, Nantong University, Nantong 226019, China
Plasmonic nanolaser as a new type of ultra-small laser, has gain wide interests due to its breaking diffraction limit of light and fast carrier dynamics characters. Normally, the main problem that need to be solved for plasmonic nanolaser is high loss induced by optical and ohmic losses, which leads to the low quality factor. In this work, InGaN/GaN nanoplate plasmonic nanolaser with large interface area were designed and fabricated, where the overlap between SPs and excitons can be enhanced. The lasing threshold is calculated to be ~6.36 kW/cm2, where the full width at half maximum (FWHM) drops from 27 to 4 nm. And the fast decay time at 502 nm (sharp peak of stimulated lasing) is estimated to be 0.42 ns. Enhanced lasing characters are mainly attributed to the strong confinement of electromagnetic wave in the low refractive index material, which improve the near field coupling between SPs and excitons. Such plasmonic laser should be useful in data storage applications, biological application, light communication, especially for optoelectronic devices integrated into a system on a chip.
Journal of Semiconductors
2021, 42(12): 122803
1 南京大学 电子科学与工程学院, 南京 210046
2 南京邮电大学 电子与光学工程学院, 南京 210023
3 南京邮电大学 微电子学院, 南京 210023
4 厦门大学, 福建 厦门 361005
基于氮化镓微米LED(Micro-LED)的可见光通信(Visible Light Communication, VLC)技术成为近年来的研究热点。通过深紫外光刻技术制备了小尺寸的氮化镓基蓝/绿光Micro-LED芯片, 深入研究了40~10μm不同尺寸Micro-LED器件的性能, 以及其作为VLC光源的调制带宽能力。研究发现, 随着LED器件尺寸的缩小, 其调制带宽显著增加。通过在电极间加入电磁屏障以及对LED器件侧壁进行钝化修复, 直径为10μm的绿光Micro-LED亮度可达1×108cd/m2, 直径为20μm的蓝光Micro-LED的调制带宽可达372.6MHz。研究结果表明, 基于氮化镓的Micro-LED芯片在调制带宽上仍有较大的提升空间, 经过进一步的研究, 有望推动高速可见光通信的系统应用。
可见光通信(VLC) 调制带宽 氮化镓 visible light communication (VLC) Micro-LED Micro-LED modulation bandwidth GaN

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute for Electric Light Sources, School of Information Science and Technology, Engineering Research Center of Advanced Lighting Technology, and Academy of Engineering and Technology, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Department of Chemistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario M5S 3H6, Canada
In this work, a blue gallium nitride (GaN) micro-light-emitting-diode (micro-LED)-based underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC) system was built, and UWOCs with varied Maalox, chlorophyll, and sea salt concentrations were studied. Data transmission performance of the UWOC and the influence of light attenuation were investigated systematically. Maximum data transmission rates at the distance of 2.3 m were 933, 800, 910, and 790 Mbps for experimental conditions with no impurity, 200.48 mg/m3 Maalox, 12.07 mg/m3 chlorophyll, and 5 kg/m3 sea salt, respectively, much higher than previously reported systems with commercial LEDs. It was found that increasing chlorophyll, Maalox, and sea salt concentrations in water resulted in an increase of light attenuation, which led to the performance degradation of the UWOC. Further analysis suggests two light attenuation mechanisms, e.g., absorption by chlorophyll and scattering by Maalox, are responsible for the decrease of maximum data rates and the increase of bit error rates. Based on the absorption and scattering models, excellent fitting to the experimental attenuation coefficient can be achieved, and light attenuation by absorption and scattering at different wavelengths was also investigated. We believe this work is instructive apply UWOC for practical applications.
220.4830 Systems design 290.5850 Scattering, particles 290.5825 Scattering theory 230.6080 Sources Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 100010
1 桂林电子科技大学电子工程与自动化学院, 广西 桂林 541004
2 广西光电信息处理重点实验室, 广西 桂林 541004
为了研究气溶胶介质多次散射效应对区域内偏振光传输特性的影响,通过CE318太阳分光计实测数据反演得到了区域内气溶胶微物理光学特性参数(光学厚度、粒子复折射率、粒子谱分布)。利用蒙特卡罗矢量辐射传输模型系统分析了粒子复折射率、粒子群有效半径、入射光偏振状态对传输特性的影响。研究结果表明:较小复折射率实部粒子的传输特性对复折射率实部变化敏感性较强;复折射率虚部是影响辐射传输特性的一个重要因素,虚部越大,吸收性越强,传输特性越差;粒子群有效半径越大,光波透射率就越低,反射率则越高;入射光偏振状态对传输特性的影响较小,相比其他类型的偏振光,水平偏振光的反射率和透射率受入射角的影响较大。
大气光学 气溶胶 多次散射效应 CE318太阳分光计 蒙特卡罗辐射传输 激光与光电子学进展
2018, 55(8): 080103
1 中国科学院安徽光学精密机械研究所中国科学院环境光学与技术重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230031
2 安徽工业大学数理科学与工程学院, 安徽 马鞍山 243032
3 安徽医科大学药学院, 安徽 合肥 230032
采用高温热解五氧化二氮(N2O5)的方法,利用N2O5与NO3自由基之间的热平衡关系,通过腔衰荡光谱技术测量N2O5及NO3自由基的浓度。基于二氧化氮(NO2)与N2O5之间平衡可逆,探讨加热温度及NO2浓度变化对N2O5分解率的影响;考虑N2O5在测量系统中的损耗,经初步的量化分析得到进气效率为88%。通过Allan方差选取最佳积分时间,在外场测量条件下,优化系统的体积分数探测限为8.6×10
-12;通过分析进气效率、吸收截面及N2O5不完全热解等不确定性因素,估算得到整体测量误差约为±10%。在合肥郊区进行夜间大气实际监测,测量期间N2O5的浓度变化范围在(0.035~1)×10
-9之间,平均浓度为4.52×10
-10。该技术为实现大气中N2O5及NO3自由基的高灵敏度在线监测提供了有效途径。
大气光学 腔衰荡光谱技术 五氧化二氮 二极管激光 热解





